? “I SELL A LOT BUT WHERE IS THE MONEY? WHERE IS MY COMPANY LOSING MONEY?”
Have you ever wondered why, despite having a high volume of sales, your company does not have enough cash flow at the end of the month?
This is a common dilemma in the business world, and often the solution lies in understanding and managing liquidity.
With the liquidity ratio we can measure the capacity of the business to meet its short-term payment commitments.
It is an essential indicator to measure the financial health and liquidity risk of the company.
LIQUIDITY MEANING AND HOW TO CALCULATE IT?
This metric determines a company’s ability to meet its short-term payments using assets that can be easily converted into cash.
High liquidity ensures that the company can handle contingencies or investment without compromising its stability
The Liquidity Ratio tells us whether a company can pay its debts due within a year with its current assets.
LIQUIDITY RATIO FORMULA.
The liquidity ratio is an indicator that measures a company’s ability to cover its short-term obligations with its liquid assets.
Liquid assets are those that can be quickly converted into cash without losing value.
This ratio is calculated by dividing the company’s current assets by its current liabilities:
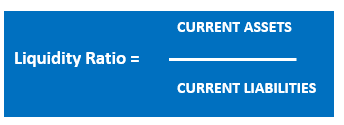
❖ Current Assets: include cash in hand, accounts receivable, inventories.
❖ Current Liabilities: short-term debts, accounts payable, creditors, i.e., all payment obligations due within a year.
LIQUIDITY RATIO INTERPRETATION.
The Ratio indicates how many euros you have for each euro you owe.
Example:
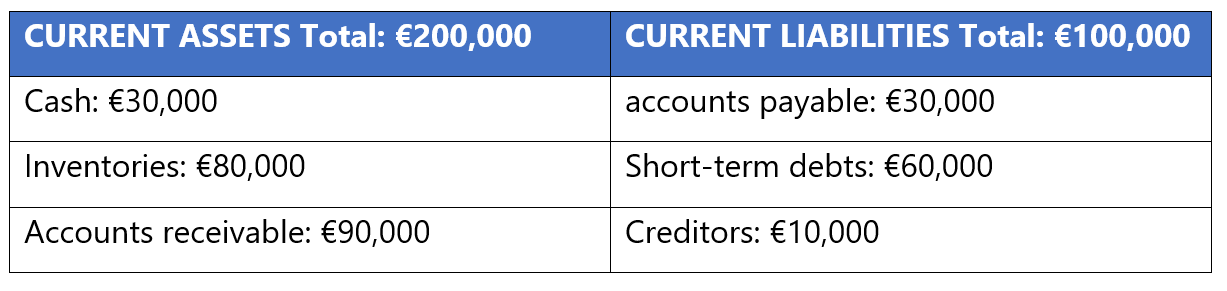
If a company has €200,000 in current assets and €100,000 in current liabilities, its liquidity ratio would be: 200,000 / 100,000 = 2.
This means the company has twice as many assets as short-term debts.
It’s a positive sign of the company’s financial health. However, it could also indicate that the company may be accumulating unproductive assets or idle resources.
IDEAL VALUES FOR THE RATIO:
Ideally, it should be between 1 and 2, as the company could cover its short-term obligations with its short-term assets.
Although 1 would be enough to meet payment obligations, we must consider that customers and inventories are not quickly convertible into cash; hence, ideally, it should be at least 2.
A ratio greater than 2 would be excessive and indicate excess liquidity that could be invested in debt repayment, dividends, share buybacks, or other assets that generate higher liquidity.
? Liquidity Ratio between 1 and 2 → optimal, as the company has 1 or 2 euros of assets for every euro of debt to cover its payments.
? Liquidity Ratio > 2 → excessive, the company may be accumulating idle resources that could be invested in other assets generating returns.
? Liquidity Ratio < 1 → risk of default, the company has more short-term debt than liquid money to pay.
OTHER RATIOS TO MEASURE LIQUIDITY
Cash Ratio or Acid Test:
CURRENT ASSETS – INVENTORIES / CURRENT LIABILITIES
It’s considered acceptable between 0.8 and 1.
Availability Ratio: CASH / CURRENT LIABILITIES
An availability ratio of 0.2 or higher is usually considered acceptable for many companies.
FACTORS AFFECTING LIQUIDITY:
- Lack of cash.
- Inefficient inventory management.
- High accounts receivable.
- Seasonal sales.
- High short-term debt.
- Drop in sales.
- High operating expenses.
HOW TO IMPROVE COMPANY LIQUIDITY
It’s advisable for the ratio to be greater than 1 but not exceed 2, as a result below indicates insufficient liquidity and a result above, a lack of profitability.
WHAT TO DO IF WE HAVE LOW LIQUIDITY:
The solution involves reducing current liabilities and/or increasing current assets:
✅ Increase sales to obtain more liquidity and rights to collect.
✅ Active Inventory Management: improve inventory management, reducing unnecessary stock, and waste.
✅ Partner Contributions: More funding through capital contributions.
✅ Improve Collection Management: Implement stricter collection policies, reduce customer payment periods.
✅ Debt Restructuring: renegotiate short-term debts to convert them into long-term debts, thereby reducing current liabilities.
✅ Negotiate with suppliers: Renegotiate terms with suppliers to extend payment deadlines or reduce prices, thereby decreasing current liabilities.
WHAT TO DO IF THERE’S EXCESS LIQUIDITY:
✅ Expand the business into other markets.
✅ Invest in fixed assets or financial investments.
✅ Pay off debts.
✅ Distribute dividends.
CONCLUSION:
Not having a good balance between a company’s assets and liabilities poses a liquidity risk by not being able to convert assets into cash quickly, leading to payment defaults. Maintaining an appropriate balance between assets and liabilities is essential to avoid liquidity risks. Poor management can lead to the inability to quickly convert assets into cash, resulting in defaults. Effective management of the liquidity ratio not only reflects the financial health of your company but also ensures its ability to face challenges and seize market opportunities.
? If you find this information useful and would like personalized advice for your company, do not hesitate to contact me. Together, we can work to strengthen the financial position of your business.